In a move that has sent ripples across the international community, the Russian President’s recent visit to Pyongyang culminated in a groundbreaking agreement between Russia and North Korea. This pact, characterized by a mutual defense clause, mandates both countries to provide immediate military aid to each other in the event of armed aggression. This development is particularly significant given the current global political climate, which is marked by escalating tensions and shifting alliances.

Issues Involved
The crux of the matter in the hearing of the Russia-North Korea defense pact lies in its potential to dramatically alter the geopolitical landscape of Northeast Asia and beyond. At the heart of the issues being addressed is the mutual defense clause, which obligates military support in the event of an armed attack against either nation. This clause, reminiscent of Cold War-era dynamics, raises significant concerns about regional security, the balance of power, and the potential for escalation in military tensions.
Furthermore, the pact’s provisions for technological and military cooperation, especially in the realm of nuclear and missile capabilities, present a direct challenge to non-proliferation efforts and international security norms. As such, the hearing seeks to unravel the implications of this pact on global strategic stability, the responses it necessitates from neighboring countries and international alliances like NATO, and the broader implications for global peace and security. The discussion is framed against a backdrop of rising global tensions and the shifting alliances that underscore the complexity of modern international relations.
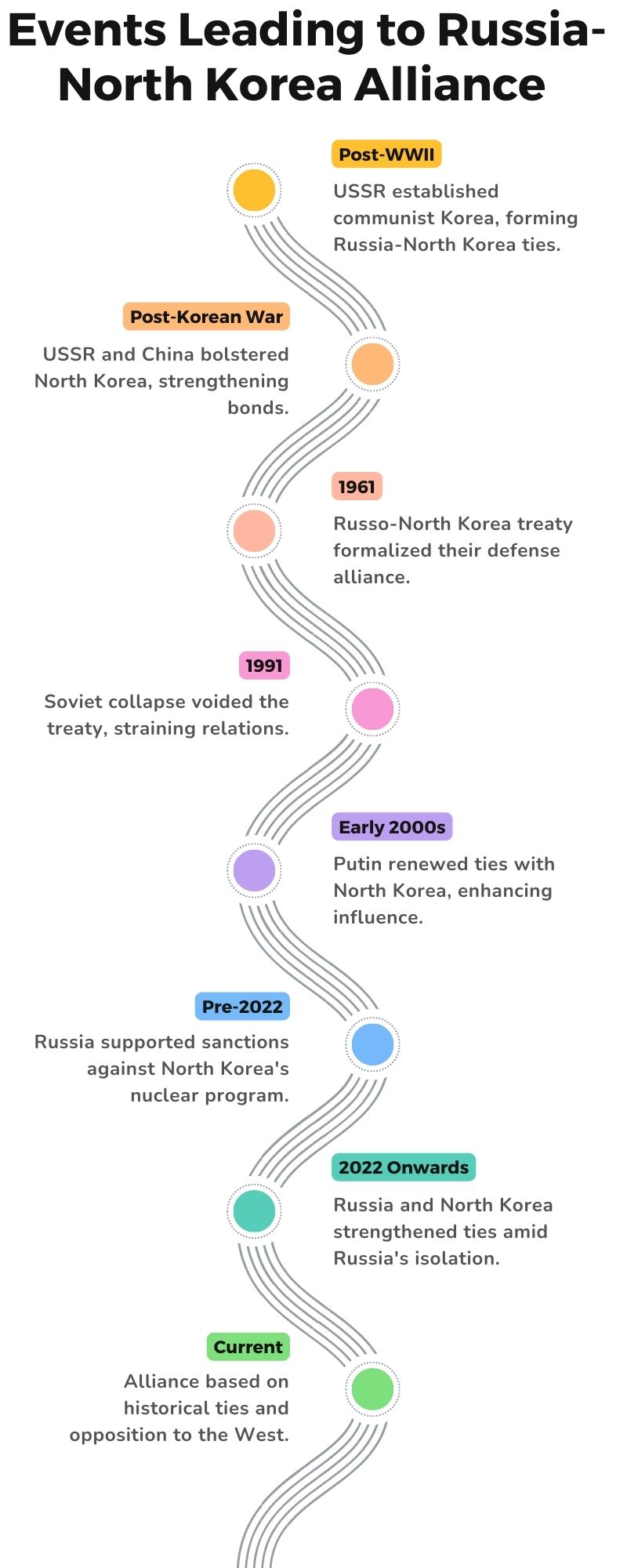
Historical Events Leading to Russia-North Korea Alliance
Post-World War II: The Soviet Union’s establishment of a communist regime in Korea laid the foundational stones of the Russia-North Korea relationship. By providing crucial military support to Kim Il Sung during the Korean War, the USSR played a pivotal role in shaping North Korea’s political landscape.
Post-Korean War: Following the Korean War, the USSR, alongside China, continued to bolster North Korea through military and economic support, further strengthening the bond between these communist states and ensuring North Korea’s survival and continuity.
1961: The signing of the Russo-North Korea Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance in 1961 was a significant milestone, introducing a formal mutual defense agreement that solidified their alliance on the international stage.
1991: The dissolution of the Soviet Union marked a turbulent period, voiding the treaty and leading to a temporary decline in relations. This period underscored the fragility and the politically driven nature of international treaties.
Early 2000s: Vladimir Putin’s rise to power in Russia initiated a renewed effort to enhance relations with North Korea, signaling Russia’s intent to maintain and strengthen its influence in East Asia amid changing global dynamics.
Pre-2022: Despite its historical ties, Russia maintained a critical stance on North Korea’s nuclear ambitions pre-2022, supporting international sanctions against its nuclear program, which showcased Russia’s complex position on non-proliferation.
2022 onwards: The strengthening relationship between Russia and North Korea amidst Russia’s international isolation due to its actions in Ukraine represents a strategic pivot, demonstrating a mutual interest in countering Western influence.
Current situation: Today, the Russia-North Korea alliance stands as a testament to pragmatic geopolitical considerations, built on a foundation of historical ties and shared opposition to the Western liberal order, amidst a global environment reminiscent of Cold War-era divisions.
Treaty on the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership Pact
The Treaty on the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership Pact marks a significant evolution in Russia-North Korea relations, embodying a comprehensive agreement that promises to deepen cooperation across various domains, with a notable emphasis on mutual military support and technological assistance.
Mutual Defense Clause: Article 4’s mutual defense obligations underscore the treaty’s strategic depth, potentially impacting global security dynamics by fostering closer weapons production cooperation and enhancing both nations’ military capabilities.
Technological Assistance: The emphasis on technological support is critical, potentially accelerating North Korea’s nuclear and missile programs by providing access to advanced technologies, thereby altering the balance of power in the region.
Key Points of the Pact
The pact enumerates several key points, from mutual respect and non-interference to a shared commitment against unilateral coercive measures, aiming to create a framework for a multipolar world order. This comprehensive approach seeks to deepen bilateral cooperation across a wide range of areas, including defense, economic, and cultural exchanges, reflecting both nations’ aspirations for a new international order.
Other Significant Agreements in the Region
China-North Korea Treaty (1961): This treaty, emphasizing mutual military assistance, highlights the longstanding alliance between China and North Korea, underpinning the strategic security dynamics in East Asia.
United States-Philippines Mutual Defense Treaty (1951): Reflecting the United States’ commitment to its allies in the Asia-Pacific, this treaty remains a cornerstone of regional security, especially amidst rising tensions in the South China Sea.
United States’ other defense agreements: These agreements, encompassing a broad network of alliances, illustrate the United States’ strategic approach to ensuring collective defense and stability in the Asia-Pacific and beyond.
United States-Taiwan situation: The informal defense ties between the United States and Taiwan, characterized by strategic ambiguity, play a critical role in the complex security calculus of the Asia-Pacific, balancing commitments under the “One China” policy with the realities of geopolitical rivalries.
Impact on South Korea and Japan’s Security Policies
Strategic Implications: The Russia-North Korea pact presents a direct challenge to the security interests of South Korea and Japan, prompting a reassessment of defense strategies and potentially accelerating an arms race in the region.
Response Measures: Anticipated defensive and policy adjustments by South Korea and Japan in response to the pact will likely include strengthening military capabilities and solidifying alliances with the United States, reflecting the heightened security concerns.
Broader Geopolitical Effects: The pact may trigger broader geopolitical shifts, with the potential for an arms race and realignment of global alliances, underscoring the complex interplay of regional and international relations in shaping security policies.
NATO
NATO’s establishment as a collective security alliance against the Soviet Union, and its expansion over the years to include 30 member states, showcase its central role in global security architecture, aimed at ensuring peace and stability in the North Atlantic area.
Recent Developments
The interest from Finland and Sweden in joining NATO reflects the alliance’s enduring relevance and the shifting security dynamics in Europe, indicating a broader concern over regional stability in the face of emerging global threats.
Conclusion
The recent pact between Russia and North Korea is not merely a bilateral agreement; it is a harbinger of the evolving geopolitical landscape, challenging the existing global order and underscoring the complexities of international relations. For judiciary aspirants, this scenario presents a unique case study in the interplay between international law, sovereign nation-states, and global security frameworks. The pact’s implications stretch beyond Northeast Asia, suggesting a rekindling of Cold War-esque divisions and a potential reshaping of global alliances. As future legal professionals and potentially judges or policymakers, understanding these dynamics is crucial. It underscores the importance of a robust legal framework that can address the nuances of international agreements, sovereignty, and the prevention of conflict. This event should encourage aspirants to think critically about the role of the judiciary in interpreting international law in the face of shifting political alliances and security threats.
Moreover, it highlights the need for legal practitioners who are not only versed in domestic law but also possess a keen understanding of international relations and the legal implications of global treaties and pacts. In navigating the complexities of such international agreements, the judiciary plays a pivotal role in maintaining the balance between national interests and global peace. This case is a compelling reminder of the critical need for a well-informed, legally astute judiciary capable of addressing the challenges of an increasingly interconnected and politically complex world.

